What is a Line Isolation Monitor?

A Line Isolation Monitor, commonly referred to as “LIM”, monitors the overall insulation of a “Line.” Line Isolation Monitors are used to monitor hospital electrical power systems typically found in critical patient areas such as ICUs and Operating Rooms.
When considering the word “Line” as it relates to operating rooms, one must consider all components in an ungrounded system. The goal of an ungrounded system is to isolate and insulate every electrical device from the grounded system. The ungrounded system is more than the outlets and wires behind the wall - everything that plugs into the outlets becomes part of the ungrounded electrical system.
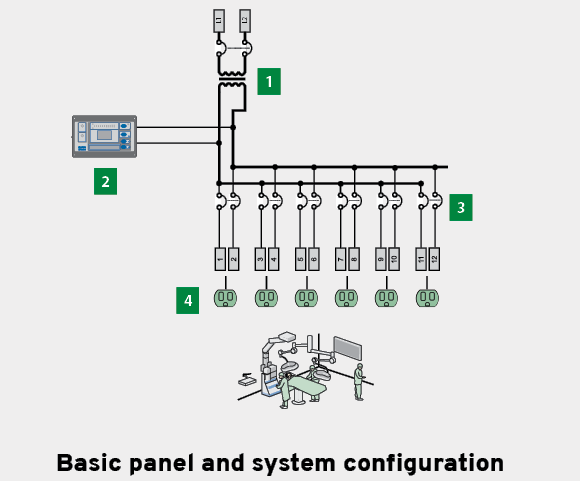
Components typically found connected to “Ungrounded Systems” in operating rooms include:
-
Receptacles (electrical outlets) distributed throughout the operating room
-
Isolation transformer secondary winding (the transformer’s primary winding is attached to a different isolated electrical system)
-
Circuit Breakers (CB) in the Isolation Power Panel (IPP)
-
The Line Isolation Monitor (LIM) is also connected to the ungrounded electrical system
Other components:
- Surgical lights within six feet of the patient
- Power cords that have insulated copper conductors (the purpose of the cord’s insulation is to keep the copper from touching “Ground”)
- Suction pumps, ventilators, Bobies - Bipolar electrocautery tools, heart and oxygen monitors
- When plugged into a receptacle, the instruments used by the medical team
There are many more components that make up the isolated “ungrounded electrical system.” In an ideal scenario, all the above components, including the power cords, will remain insulated from ground. Unfortunately, we don’t live in an ideal world, things go wrong, insulation wears off, wire connections come loose and components on circuit boards fail resulting in ground faults. Because of this, Bender Line Isolation Monitors are considered an essential part of any state-of-the-art hospital.
Listed below are keywords that are related to this topic.
Keywords:
- Monitor: To continuously observe and check the quality of electrical insulation.
- Isolation: The process of separating or isolating two electrical systems.
- Line: The “Line” is isolated from “Ground” and monitored with respect to “Ground.” When we see the word “Line”, we might think of a set of power lines or wires (conductors) carrying electrical power to a devices (loads). While the wires and devices are a portion of what is referred to as the “Line”, there are many more components that are assumed when the word “Line” is used by engineers and electricians. The word “Line” as it relates to this blog, is a simple label referring to a complex subgroup of components.
- Ground: A reference point in an electrical system usually bonded to earth ground or building ground.
- Grounded vs. Ungrounded: In order to develop an understanding of an “Ungrounded System”, we must first define what a “Grounded System” is.
- Grounded [Electrical] System: An electrical system is considered grounded when at least one conductor or point in the Electrical System is [galvanically] attached to Ground.
- Galvanically: An adverb occasionally used to state that a component or system of components can be conductive. Components that are “galvanically attached” can allow electrical current to flow through them.
- Here in the United States, most of our residences and commercial buildings have “Grounded Systems.”The electrical systems are attached to ground at one point, typically the neutral point on a transformer’s secondary winding.
- Ungrounded [Electrical] system: An electrical system is considered ungrounded when all points of the electrical system are galvanically isolated / insulated from Ground.
- Insulator: Examples of “Galvanically Isolated” could be insulating materials such as plastic, rubber, ceramics or type XHHW wire insulation. These types of materials are intended to provide an insulating barrier and prevent the flow of electrical current to ground and through humans.
- Since most systems in the States use grounded power, most people tend not to be familiar with the advantages of “Ungrounded Systems.”
- Isolation Transformer: An isolation transformer is a special transformer used to isolate an electrical system from ground. The secondary winding of an isolation transformer is also the power source in an ungrounded electrical system.
- Fault: Insulation failure or an electrical component failure.
- Ground Fault: Something that was supposed to be isolated touched ground.
- Alarm: A signal (such as a loud noise or flashing light) that warns or alerts of a hazardous condition.
For more information about this application or to learn more about Bender technology related to your specific application, contact our team of experts.
This article is for informational purposes only. Bender provides the information "as is" without warranty and is not responsible for its accuracy or reliability. No warranties are given regarding its suitability for any specific circumstances.

.jpg)
-1.jpg?width=352&name=Blank%20300%20x%20175%20(3)-1.jpg)
.jpg?width=352&name=Blank%20300%20x%20175%20(7).jpg)
